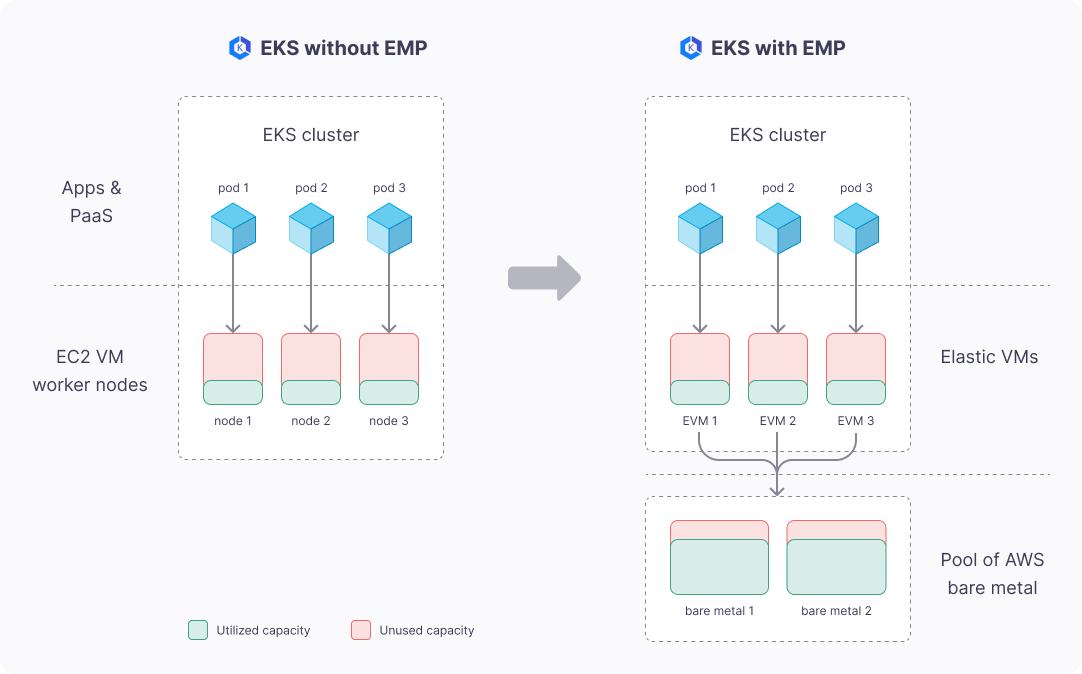
How EMP Works
EMP optimizes EKS utilization and cuts costs by deploying its own Virtual Machines on EC2 metal instances— all fully automated, behind the scenes, and from within your AWS account.
Resource Over-Commit
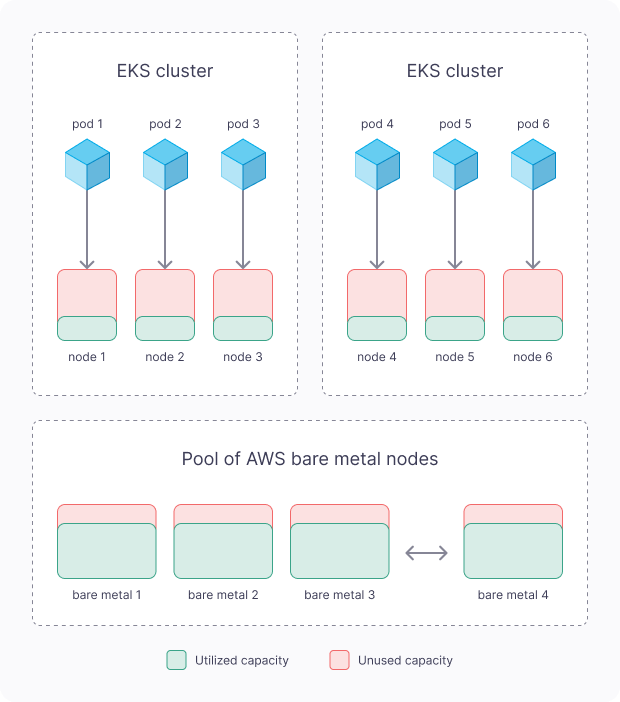
- EMP deploys an alternate virtualization layer, using AWS bare metal underneath, creating “Elastic VMs” (EVMs), that look and feel exactly like regular EC2 VMs.
- Behind the scenes, EVMs are optimized for best resource utilization. EMP packs more EVMs on fewer bare metal nodes using virtualization level resource over-commit, based on actual VM resource usage metrics.
- This gets rid of both bin-packing overhead AND removes the need to tweak your applications resource requirements.
Utilization Aware Rebalancing
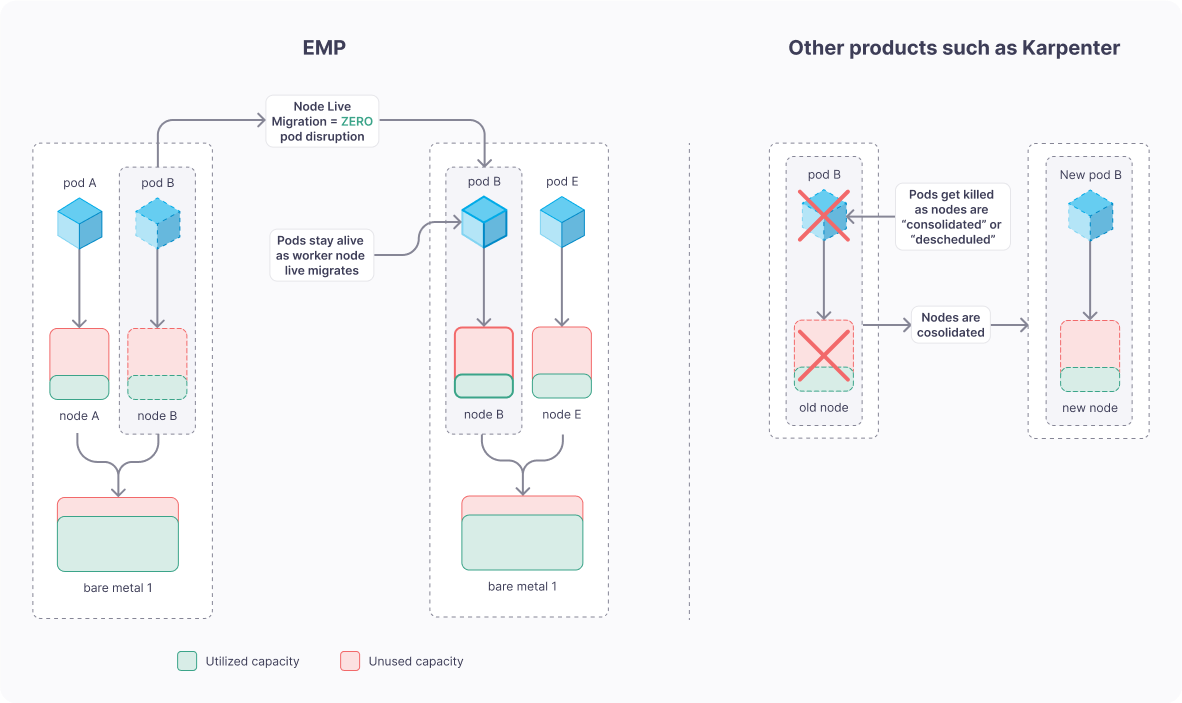
- When the resource usage for the EVMs on a bare metal node starts going up, EMP will “live migrate” some EVMs to another bare metal server.
- This is done using real-time metrics and historical usage trend pattern.
- Your pods stay alive without churn and app SLA is not compromised.
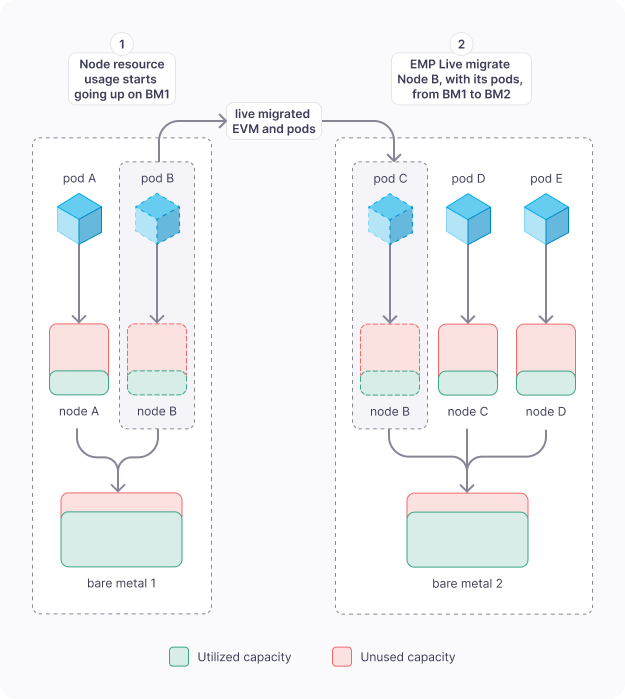
Zero Pod Disruption! We Mean It.
EMP optimizes EKS utilization and cuts costs by deploying its own Virtual Machines on EC2 metal instances— all fully automated, behind the scenes, and from within your AWS account.
EMP vs Existing Tools
| Outcomes | EMP | Karpenter | CloudHealth | Cloudability | CloudZero | Kubecost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Improve resource efficiency using over-provisioning | ||||||
| Scale workloads without pod disruption | ||||||
| Eliminate constant Requests and Limits updates | ||||||
| Optimize usage via bin packing | ||||||
| Cost visibility | ||||||
| Resource tagging | ||||||
| Cost allocation |
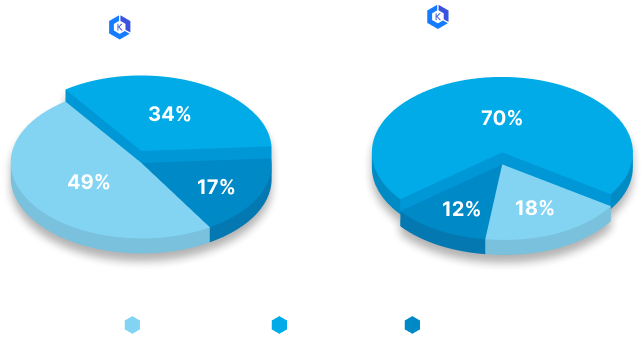
Achieve over 70% utilization with EMP
Contact US